There are moments in the Middle East when history suddenly shift gears and takes us all by surprise. Lenin knew the cadence: there are decades, he wrote, where nothing happens; and then, weeks in which decades happen. A year ago, Syria – trapped in the vortex of its civil war for almost fourteen years and virtually ignored by the rest of the world since October 7 2023 – suddenly leapt into one of those crazy weeks, leaving allies, enemies, and analysts alike blinking in the dust. Even now, a year after the astonishing fall of Damascus, the country sits like Kipling’s Tomlinson at the gates of judgement: not quite damned, not fully redeemed, suspended between heaven and hell.
Sleepers awake …
For years, as The Independent’s Bel Trew observed last December (see Syria. Illusion, delusion and the fall of tyrants) the world forgot about Syria – notwithstanding the courageous efforts of western and Syrian reporters and humanitarian workers who strove in perilous circumstances to bear witness. The civil war had become the background hum of the region, a grim drone many had learned to tune out as Ukraine and Gaza dominated the world stage. The regime of Hafez al Assad, brutal and immovable, bolstered by Russia, Iran and Hezbollah, looked set to endure indefinitely. The jihadi rebel enclave in Idlib, though supported by Türkiye, was dismissed as a besieged hold-out. Even those who professed expertise couldn’t reliably tell you whether the war was still ongoing, who was fighting whom, or what stage the conflict had reached. It was as if the wheels of war had stopped spinning.
Then, over the space of days – eleven, to be precise – the wheels spun again. Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham’s fighters burst from their confined redoubt with a momentum no one expected (including, it seems, themselves), sweeping through Aleppo and racing down the highway to the capital. Analysts reached instinctively for historical parallels: Havana 1959, Saigon 1975, Kabul 2021. Analyst David Kilcullen pointed instead to Timur Kuran’s theory of the “preference cascade”: the sudden collapse of a regime that had mistaken silence for loyalty and compliance for consent. Assad’s security apparatus – omnipresent, omniscient, yet somehow oblivious – realised too late that its soldiers had no stomach left for the fight. The all-powerful giant had feet of clay.
It didn’t help that Iran, Assad’s indispensable patron, had stumbled into the most grievous strategic miscalculation of its post-1979 history. Flush with revolutionary zeal, Tehran had kicked the hornet’s nest in Lebanon, prompting Israel to pivot from Gaza to Hezbollah with stunning force. Suddenly Iran’s expeditionary assets were exhausted, its proxies over-extended, and its clerical leadership exposed as both ageing and isolated. Even the Ayatollah’s conspiratorial refrain – that the fall of Damascus was all a plot by the Great Satan, the Little Satan, and the Sultan in Ankara – couldn’t mask the fact that this was less Zionist cunning than simple imperial overreach. When the rebels came, neither Iran nor Hezbollah, nor Russia, entangled in its Ukrainian quagmire, could ride to the rescue.
But the rebels, too, were surprised. Their mandate from Ankara was modest – expand the borders of their statelet a little, test the regime’s nerve. Instead, they found themselves virtually unopposed on the road to Damascus. In an Informative article in E-zine Unherd republished below, British writer and investigative journalist Tam Hussein writes how many of the fighters interpreted the victory as divine intervention – not jihadi zealotry, but a sincere theological attempt to explain the inexplicable. The suddenness of Damascus’s collapse felt, to them, like an echo of Muhammad’s bloodless conquest of Mecca. And in a land where the eschatological imagination has always saturated politics, it didn’t take long before social media brimmed with end-times speculation. Ahmed al Shara’a – formerly Abu Mohammad al-Jolani, with a $10 million American bounty on his head – was seen by some as “the one”, and the precursor of the Mahdi and the foretold end of days.
Yet as Hussein rightly notes, miracles make poor policy. The survival of the new Syrian administration will depend not on prophecy but on governance, and on whether Shara’a, interim president and ex-jihadi turned statesman, can transform a miraculous seizure into a sustainable state.
To his credit, he has avoided the catastrophic purges that helped destroy post-invasion Iraq. He has kept the civil service intact, flirted audaciously with Western diplomacy, and allowed at least the theatrical semblance of elections. He has restored the embassy in London, opened channels to Washington, even visiting the White House and played the charm-game with Gulf capitals that only recently readmitted Assad into their fold. As Hussein writes, he has shown political finesse: keeping the constitution, appointing seventy parliamentarians himself, and balancing piety with pragmatism.
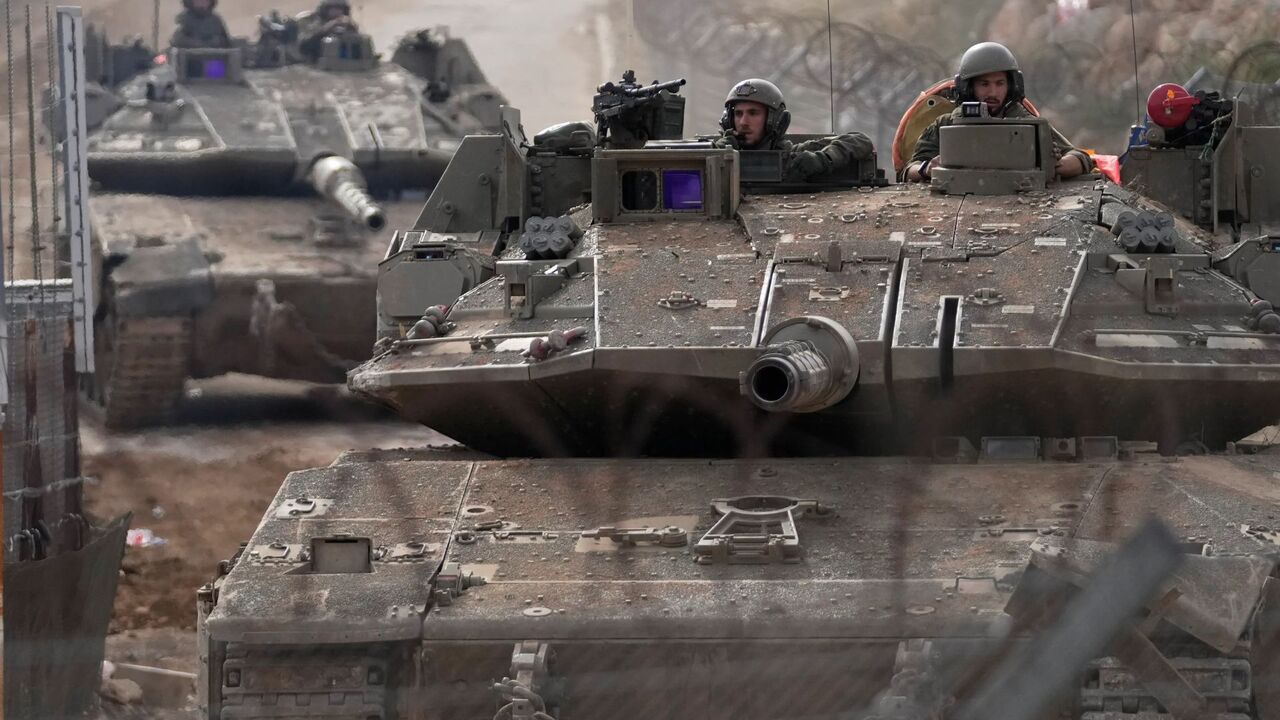
But the tightrope is frayed. Sectarian wounds – Druze, Alawite, Sunni, Christian – remain raw and unstitched, with the Latakia massacres now entering their fraught judicial phase, and Israel stirring the Druze pot. Kurdish anxieties simmer: the old “Arab-first” chauvinism must be abandoned if Syria’s patchwork is ever to become a tapestry again. Foreign fighters, once lionised, now loiter between hero and hazard, implicated in sectarian atrocities. Kurds clash with Syrian forces; Turkish troops press deeper into Rojava; Israel remains the unpredictable neighbour bestride the Golan; and Iran, though weakened, is never entirely out of the game. It is not inconceivable that the forces that helped topple Assad could yet turn their sights toward Jerusalem in the belief that prophecy demands it.
And there are darker portents too – those flickering shadows that hint the wind of freedom may be blowing from the wrong quarter. The new government’s early gestures toward Islamisation – the hair-covering admonition, the curriculum purge, the dismissal of women from key posts, the torching of a Christmas tree in Hama – suggest that pro-Russia and anti-western platforms like RT and Mint may have a point when they warn that the leopard has not fully changed its theological spots. Shara’a’s declaration that elections may be four years away, the dissolution of the old constitution, and the folding of all rebel factions into state structures recall less a liberal transition than a consolidation of revolutionary power.
Meanwhile, the country remains a mosaic of mini-wars. In the north, Turkish proxies grind against Kurdish forces in Rojava. In the south, local militias continue to resist HTS’s claim to national authority. In the west, Alawite formations cling to their shrinking redoubts. To the east, Islamic State survivors eye the chaos, waiting for the prison gates to break. And overhead, as ever, the Americans and Israelis fly their competing deterrents, ensuring the war never quite ends.
So: Syria stands at the crossroads. Will Syria’s future be heaven, hell, or merely another circle of the inferno?
Optimism is possible – cautiously so. If the West can avoid its habitual fatalism, if, when sanctions are lifted, investment flows, if Turkey and Israel can be coaxed into tolerable coexistence, if Kurdish autonomy is honoured, if sectarian grievances are handled with equity and not vengeance — then Syria could, in time, become a conservatively stable hub. Shara’a’s Idlib experiment shows he can build an economy under duress.
But the inverse is equally imaginable: a Lebanon-style implosion, a Yugoslav-style partition, or a Gaza-style fortress of permanent mobilisation. As Isreali commentator and contributor to Haaretz Zvi Bar’el wrote a year ago, writes, the warm international “envelope” around Damascus is generous but tentative. Nobody quite knows where Shara’a is heading. They simply assume anyone is better than Assad – the same mistake Syrians once made about the old Ba’athi patriarch Hafez al-Assad himself.
Right now, the future’s not ours to see. Something’s happening, but we don’t know what it is, and anyone with a deep knowledge of the Middle East knows that one must expected the unexpected. The old regional wars – Gaza, Lebanon, the Red Sea, Iran’s Axis of Resistance – though seemingly on hold, have not paused to let Syria breathe. The war in Ukraine grinds into winter, the bizarre Gaza peace plan shuffles on, and there are constant political shifts in Washington. Each of these could rewrite the geopolitical chess board yet again.
Still, as Robert Fisk wrote in the final line of the final book he never lived to promote: all wars come to an end, and that’s where history restarts. Syria is restarting now – painfully, precariously, imprecisely – but restarting nonetheless.
Whether Syria walks toward heaven or hell remains to be seen. The choice – as ever in the Levant – will not be its alone.
Syria Today: Walking Through the Wreckage
A year after the Assads fell, Syria still moves through its own ruins – startled by its freedom, and half-afraid of it. The dynasty’s collapse ended the nightmare but did not usher in a dream; it simply exposed, in unforgiving daylight, the damage done over half a century of dictatorship and more than a decade of war. The smashed cities are visible to any passer-by; the deeper wreckage – the traumas, resentments, and debts of blood – is harder to map and harder still to mend.
Sednaya prison’s opened gates remain the sharpest indictment. The men who stumbled out were not just survivors but witnesses, their bodies forcing the nation to acknowledge what many had whispered and few had dared investigate. Yet even this reckoning has not united the country. Sectarian reprisals and atrocities on the coast, more atrocity and calls for Druze autonomy demands in Sweida, tribal restlessness in the south and northwest, Kurdish self-rule in the north, and Alawite fear of collective punishment keep the national psyche taut and divided. Bitterness circulates like a second economy.
The economy, meanwhile, balances on a fraying tightrope. Western aid and investment have brought cranes, reopened highways, and a flicker of commerce, but also inflation that is hollowing out households. Reconstruction glimmers like a desert mirage: real enough to chase, never close enough to touch. Corruption accompanying nepotism and patronage has survived the revolution, and many returnees discover that rebuilding a home now costs more than earning one.
Politically, the country sits in an improvised equilibrium. Al Shara’a rules as both liberator and question mark – trusted by some, tolerated by others, watched by all. His pivot toward Washington, his quiet coordination with US forces, and his break with former comrades offer a new direction, but also a gamble. Around him, sovereignty is nibbled at the edges: Israel digs deeper into Quneitra province; Türkiye tightens its grip in the Kurdish north. Liberation has shifted the map without fully restoring control over it.
So Syria stands on the threshold, like Tomlinson, neither damned nor redeemed, simply called to account. The war is over, but its aftershocks and tremors linger in regional loyalties, local vendettas and regional manoeuvres. The people are free, yet unsure of that freedom’s limits and what it asks of them. And the vast machinery of the state still creaks with old habits and temptation.
And yet – a small, highly qualified yet – Syrians are imagining a future again. Not the predetermined script of dictatorship, nor the fatalism of war, but something open, negotiable, theirs’. For a people long told that nothing changes, the mere possibility of change is its own quiet revolution. Hope is not guaranteed; neither is stability. But the impossible has already happened once, and that alone shifts the horizon.
Postscript: the strange, messianic weather of revolutions
Among the HTS fighters Tam Hussein describes, the astonishingly swift and almost bloodless collapse of Damascus could never be reduced to battlefield arithmetic. After over a decade of stalemate and slaughter, the conquest of Damascus and the fall of Assad felt too abrupt, too neat, too historically implausible to be merely human. And so they reached, perhaps instinctively, for the vocabulary of prophecy that has long circulated in the Levant: the old stories of tyrants toppled in the final days, of a just ruler rising at history’s eleventh hour, of a brief season of peace before a climactic confrontation with “the Romans,” a term that in popular imagination now stretches elastically to include Israel, America, or the West at large.
In this folk-level cosmology – not the carefully parsed doctrine of scholars, but the lived, emotional scripture of men who have lived too long fear, death and loss loss – the victory in Damascus reads like a prophetic epic ballad. When a fighter told Hussein that Syria would enjoy “ten years of peace before the war with Israel,” he was drawing from a hazy amalgam of hadith traditions and battlefield folklore to make sense if the improbable: the idea of a lull before the storm, a breathing space before the world tilts into its final reckoning. It is vernacular eschatology, shaped as much by trauma and longing as by text.
Within that register, the murmurs that Shara’a/Jolani might be “the one” carry an unmistakable Mahdist echo. No fatwas or proclamations like when Da’ish leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi famously declared the caliphate from the minbar of Mosul’s al-Nuri Mosque in 2014; but the emotional charge behind the phrase is unmistakabl: an intuitive reach for a Mahdi-shaped idea of the righteous restorer, the unifier, the man who appears when everything has fallen apart. It’s not that anyone literally thinks Jolani is the Mahdi; it’s that the mood of the moment makes such thoughts feel briefly within arm’s length. A silhouette on the horizon, nothing more.
And here, Syria is not unique. Revolutionary periods everywhere – the Protestant Reformation, the French Revolution, the Russian Revolution and Civil War, the Arab Spring even, have their magical phase — those jittery days when people begin to speak as if the world has cracked open, meaning is pouring through the seams, and events blur into myth. When a regime that seemed immovable collapses in a fortnight, people fall back on stories larger than themselves. Sudden upheaval, long suffering, and the ascent of a charismatic figure combine to crack open the ordinary world. Prophecy offers a narrative frame when history seems to be behaving like fable.
So the eschatological edge in these fighters’ conversations tells us less about doctrine and more about psychology. It’s a very human response: a form of magical thinking that arises when reality becomes too strange to process, a way of giving shape to chaos, of telling themselves that their suffering fits into a larger story. A coping mechanism, if you like – a mythic vocabulary for a moment when Damascus fell, and the ordinary rules stopped making sense and the earth seemed briefly to tilt on its axis.
See also in In That Howling Infinite, Syria. Illusion, delusion and the fall of tyrants and Cold wind in Damascus – Syria at the crossroads. And on the subject of messianism in general, see A Messiah is needed – so that he will not come
Will civil war return to Syria?
Its future is in the balance
A few months ago in Damascus, I discovered a medieval hospital. The door had been left slightly ajar, and I wandered in with my companion Hassan Idlibi — a rebel fighter and old friend. He hadn’t been in the Old City since the fall of Syria’s capital, exactly a year ago today. “When Damascus fell,” he told me, “we were at our lowest ebb. Even the attack on Aleppo was our last gasp. We wanted to break the stalemate. And then we just pushed and pushed, and we ended up sleeping inside the Umayyad Mosque. It was a miracle.”Idlibi, like many Syrians, did not interpret the taking of Damascus through geopolitics — but as divine intervention. This wasn’t because he was a mindless zealot. Far from it. He is one of the most well-read men I know. But, to his mind, the fall of Damascus was so sudden, so unexpected, that only the miraculous could explain it. The victory, he noted, had been achieved by those who had been motivated by Islam. Help had come from foreign fighters, the mujahideen, who travelled from across the globe to aid their co-religionists. And the campaign had been led by a former jihadi, Ahmed al-Sharaa, now the interim president of Syria. At the time, the old al-Qaeda operative, then known by his nom de guerre, Abu Mohammad al-Jolani, had a $10 million American bounty on his head.
After more than a decade of slaughter, no one had expected the capital to collapse. Assad, then president, had seemed like a stubborn wart: unpleasant but immovable. Jolani’s rebel enclave in the northern city of Idlib looked too small, too besieged, to pose a serious threat — though in fact it was performing better economically than inflation-ravaged Damascus, helped along by a reliable flow of Turkish hard currency. I myself expected the rebels to negotiate. What leverage did they have? Yet this rebel government, roughly the size of Croydon, took over the instruments of state, and since then has avoided stumbling into a new civil war.
The unexpected and largely peaceful victory was attributed to piety, prophecy, steadfastness. Some have even compared the final conquest of Damascus to Muhammad’s bloodless conquest of Mecca in 630. The idea of a “miracle”, here, is not mere rhetoric — it shapes political expectations. Some Syrians, at least based on my social media, think all this makes Sharaa “the one”, with my Facebook messages and WhatsApp chats awash with prophetic readings of the present. One believed Syria would now enjoy 10 years of peace before the war with Israel begins. Perhaps, he suggested, this was the prelude to the end of times. After all, so-called “Greater Syria” — encompassing much of the Levant — plays an important role in the Syrian and indeed Muslim sacral imagination. It is where prophets walked and is the place where many of the end of times narratives will play themselves out.
Yet if the fall of Damascus seemed miraculous to many Syrians, the survival of the new administration will depend less on providence than on governance. Despite his past, Sharaa has so far demonstrated an unexpected level of political finesse. He has kept the constitution, held elections — albeit with 70 seats appointed by himself — and all the while has acted the statesman. He is savvy enough to not mind having President Trump spray his latest fragrance on him in the Oval Office, or Syrian Jewish rabbis blessing him.
Sharaa has made some promising early decisions. By keeping the civil service intact, he has avoided the catastrophic purge that helped destroy post-invasion Iraq. He should continue recruiting highly-educated young Syrians from the diaspora — people familiar with Western administrations and political norms. Even so, the administration still has a tendency to fear scrutiny and behaves as if under siege. It should welcome a regulated free press, which would expose blind spots, not undermine authority. The British press has reported that Jonathan Powell’s Inter Mediate is working with the new government. This should be welcomed rather than criticised — not only for reasons of conflict resolution and soft power, but for its value in statecraft and building institutional capacity.
Sharaa’s priorities for the coming year are clear. The country remains immensely fragile, caught in a regional tug-of-war between Israel and its neighbours, and divided along ethnic and sectarian lines. The situation could easily drift into a reprise of Lebanon’s civil war. Sharaa’s first task is therefore to mend Syria’s sectarian and ethnic fractures with a sense of equity. The trials that began this month over the coastal massacres in Latakia will be an important test of how the country intends to move forward. The Druze and Alawite communities — already bruised by conflict and mistrust — require justice delivered without the language of sectarianism.
Meanwhile, Kurdish anxieties must be addressed by ending the Arab-first ideology of the old regime. Syria has never been a purely Arab country: even its favourite son, Saladin, the builder of that hospital I visited and whose grave in Damascus still draws multitudes, was a Kurd. Last year’s tentative permission for Kurdish new year celebrations (Newroz) suggests that a more pluralist future is possible. Yet it remains unclear how far Kurdish cultural expression will be allowed to develop. Already this month, exchanges of fire between Syrian government forces and Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) units under Kurdish command show how fragile the situation is.
Perhaps the most difficult balancing act involves the foreign fighters who fought on Sharaa’s side. They carry immense symbolic weight in Syrian society — and are the cause of immense fear in the West. Many are ready to resume normal life, but others still see themselves as Islam’s warriors. Recent clashes in the Idlib countryside involving French foreign fighters reflect anxieties that any rapprochement with the West might see them handed over to their home governments. The image of Sharaa standing beside Trump, receiving a symbolic “anointing” of his new fragrance, alarms them even if such engagement is politically necessary.
Granting these fighters legal status, regularising their papers, integrating some into the national army or demobilising them with stipends and educational opportunities — not unlike the GI Bill for US veterans — could go a long way toward neutralising one of Syria’s most volatile pressures.
Then there is the conundrum of Israel. On this, Sharaa has cultivated deliberate ambiguity. At the United Nations, Syria has repeatedly noted its restraint regarding Israel’s illegal strikes on Syrian territory, yet Sharaa has resisted pressure to join Trump’s flagship Abraham Accords. Signing them now would be political suicide. But ambiguity buys him room to manoeuvre — and time to consolidate the state. The question is how long this can last.
For its part, the West has worked to prevent Syria from sliding into another civil war — one that would inevitably spill over into Europe, potentially replaying the exodus of 2015. With regional partners like Saudi Arabia and Turkey, Western governments have effectively restrained Israeli escalation, aware that renewed instability would eventually reach Jerusalem’s door. It’s not impossible to imagine rebels, having overthrown a “pro-Western stooge” like Sharaa and aided by foreign fighters, actually marching toward Israel, convinced that “the infidels” will never allow them to determine their own future. As they did in Damascus, so too — in their imagination — must they do in Jerusalem.
Thus far Sharaa has governed with surprising openness. He has welcomed Britain’s foreign secretary David Lammy, met American diplomats and General David Petraeus, played basketball with US soldiers, and cooperated in counter-terrorism operations. He has also restored relations with London, with foreign minister Asaad al-Shaibani reopening the Syrian embassy.
If Western governments refuse to work with him because of his Islamist roots, they will share responsibility should Syria fracture again. Sharaa’s past is not erased; he may remain an uncomfortable partner. But what is the alternative? That he be excluded from political life and drift into a Castro- or Maduro-like role on the sidelines? If the Saudi Crown Prince can be brought in from the cold after the Khashoggi murder, then almost anything is possible.
Here I recall a meeting with former Saudi spy chief Turki al-Faisal in his South Kensington apartment after the release of his memoir. Faisal lamented how his advice went unheeded after the Afghan-Soviet war. He had urged the international community to launch something akin to a Marshall Plan — an investment programme to stabilise Afghanistan. Had that happened, the region might not have unravelled. Instead, the country collapsed into years of civil war.
Likewise, fully lifting sanctions on Syria and providing a major investment programme, coupled with training and cultural exchange, could restrain the country’s more radical elements. Reining in Israeli escalation, de-escalating the Druze conflict, and mediating between the SDF and Damascus would all help prevent new wars. On this, the West could also spare itself a future security headache by helping Damascus regularise or demobilise foreign fighters rather than leaving them to drift. This would all help to displace messianism.
What, then, would such investment bring the West, beyond avoiding another gaping wound on its eastern flank? For sure, it will not turn Damascus into another Beirut, a place for foreign journalists to party, nor into a Deano-friendly Dubai. Syria will likely remain socially conservative, more like Muscat in Oman. Given time, however, it could become a commercial hub with a distinct cultural life, just as it has been for much of its epic history. This isn’t mere optimism: Sharaa turned Idlib, once a distant town, into a magnet for Damascenes seeking commercial opportunity. Investment now would bring the West a friendly partner, business prospects and political influence. The choice is stark. With support, Syria could become a kind of West Germany: rebuilt, integrated, and stable. Without it, the country risks becoming a new Jerusalem — a battleground charged with fire and prophecy.
Tam Hussein is an award winning investigative journalist and writer. His work has been recognised by the Royal Television Society Awards.